Companies worldwide faced more cyber attacks in 2023. This was noted by Check Point Research researchers in their annual review.
Last year, organizations had to deal with more cyber attacks. This is the conclusion of Checkpoint Research specialists in their annual report.
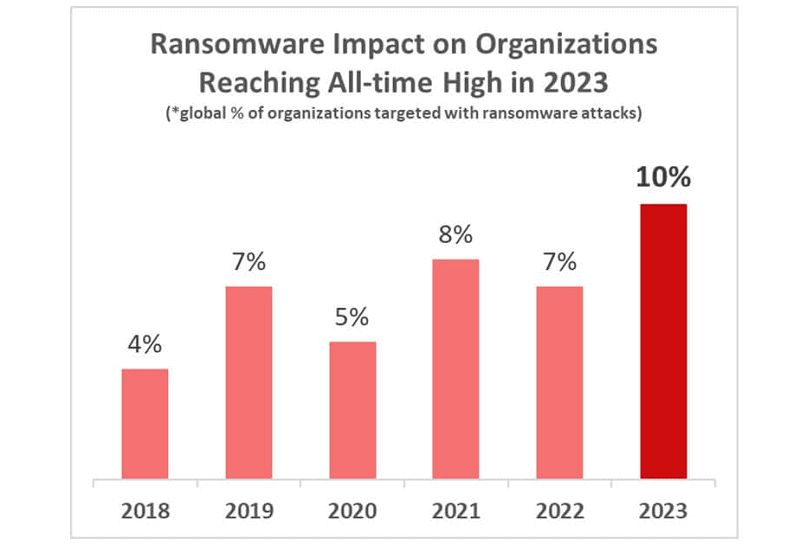
More specifically, one in 10 companies experienced a cyber attack last year. This was 33 percent more than in 2022. Then, one in 13 companies faced a cyber attack.
Interesting ransomware trends
Ransomware was the biggest culprit, according to Check Point Research. During 2023, ten percent of companies affected by a cyberattack experienced attempted installation of ransomware. In 2022, this percentage was still at seven percent.
The researchers noted several interesting trends in the number of ransomware attacks. First, the number of very large ransomware attacks increased in the past year.
In addition, the researchers discovered that since 2023, the strategy of ransomware attackers has been changing. They often carried out an attack in which data was stolen rather than files got encrypted. With this stolen data, ransomware gangs were much more likely to try to extort their victims. They had to pay up in order to keep the data private. This change in tactics became evident in the infamous MOVEit and GoAnywhere attack campaigns, among others.
Sectors affected
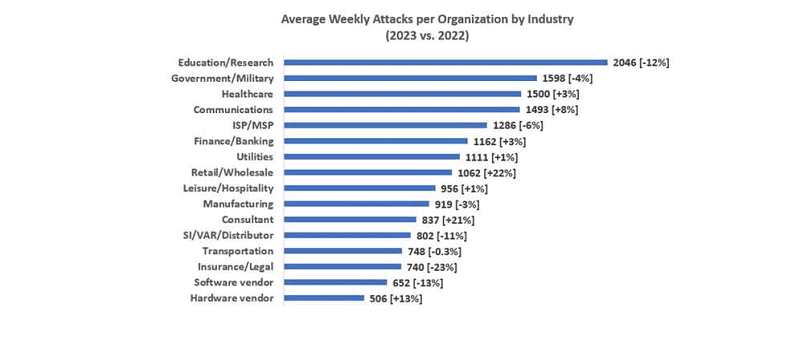
The main sectors targeted by cyber attacks in 2023 also changed. While the education and research sectors previously recorded the most attacks, attacks on these sectors declined in 2023. However, they still remain the most attacked sectors.
Attacks on retail and health care, on the other hand, increased significantly, according to the researchers. This would also represent a change of course by cybercriminals.
Advice Check Point Research
The researchers advise companies to take necessary measures to ensure that they can escape increasing cyber-attacks. These include more robust data backup, keeping workers up to date with cyber awareness training, consistent patching, better user authentication applications, more anti-ransomware applications and better threat detection in general.
Also read: How ransomware has become cybercrime’s star player