LLMjacking has been taking off recently, Sysdig notes. For example, accounts for access to DeepSeek’s LLMs were hijacked within days to hours by malicious actors who started using them for things other than intended.
Large-scale use of LLMs can be quite costly. As a result, hackers look for alternative ways to save money. Hijacking LLM accounts of ordinary end users, LLMjacking, is a good option for this. This is the finding of researchers at Sysdig.
By hijacking OpenAI, Anthropic accounts or those of other providers, the malicious can then use this capability at the original account owners’ expense to generate images, circumvent national bans on the use of LLMs and more.
Account owners of all AI providers face this form of cybercrime. For example, recently paid (API) accounts of the very recent DeepSeek-V3 and DeepSeek-R1 models have already been hijacked by malicious actors and used for other purposes at the original users’ expense.
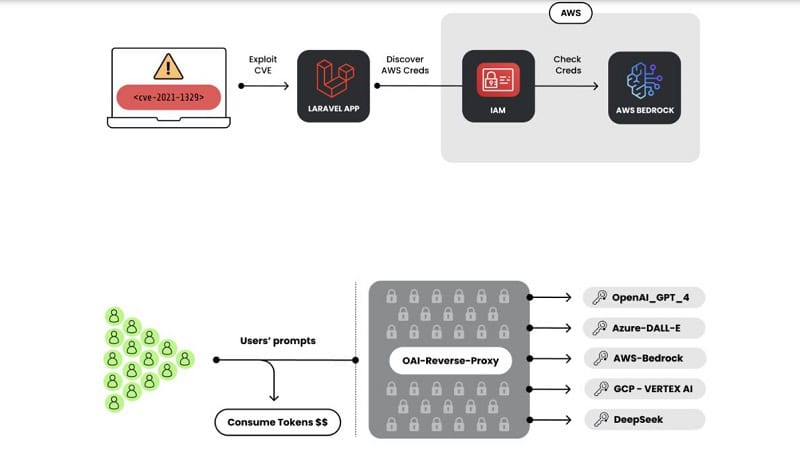
Attack path for LLMjacking
Hackers are actively looking for LLMjacking login credentials for LLMs or API keys that link to specific LLM applications. Once they have these, they use scripts to verify that these login credentials actually provide access to a desired LLM.
Then hackers put the stolen authentication data into what is known as an “OAI reverse proxy (ORP). An ORP forms a kind of bridge between an end user and an LLM, thus providing a layer of operational security.
Since their introduction in 2023, these ORPs have been increasingly modified and now offer hackers more protection from discovery. Think password protection, hiding mechanisms, and eliminating prompt logging. In addition, proxies are protected via Cloudflare tunnels that generate random and temporary domains to hide the ORP’s virtual private server or malicious IP addresses.
Malicious ORPs are mainly abused through communication channels such as 4chan and Discord. Countries such as Iran, Russia, and China use ORPs to access LLMs that are otherwise blocked to them.
Furthermore, ORPs have been modified to avoid overcharging on a single account, which would then quickly raise an alarm about abuse. The research by Sysdig’s specialists shows that some ORPs abused as many as 55 different DeepSeek APIs, in addition to APIs from other AI chat tools. By using so many keys for different apps, ORPs can take advantage of load balancing and, in this way, spread the abuse very thin.
Big problem in the making
The researchers indicate that LLMjacking is becoming a big problem. Especially now that large cloud providers such as AWS and Azure are starting to offer DeepSeek models in their Amazon Bedrock and Azure AI Foundry environments.
Therefore, the security specialists are calling for quick thinking on how best to combat these types of attacks and especially to better protect end users from them.
Also read: GhostGPT: rogue chatbot helps cybercrime