Lilac’s technology helps data scientists understand and modify text datasets.
With Lilac’s open-source tool, Databricks may further support large language model (LLM)-based systems. Lilac can evaluate LLM output and prepare unstructured datasets for model training. However, according to Databricks, analyzing unstructured text data is now too cumbersome and extremely difficult. “Historically, this process has been marred by manual, labor-intensive methods that lack scalability. Not only are these traditional methods time-consuming, but also so daunting that they deter many from attempting them,” Databricks said.
Lilac’s technology streamlines this process. To do this, the tool relies on clustering, using an AI model to analyze documents. It then categorizes similar documents into groups to generate a description for each group. For example, it can classify that three-quarters of training data come from papers, while the remaining 25 per cent is another type of data.
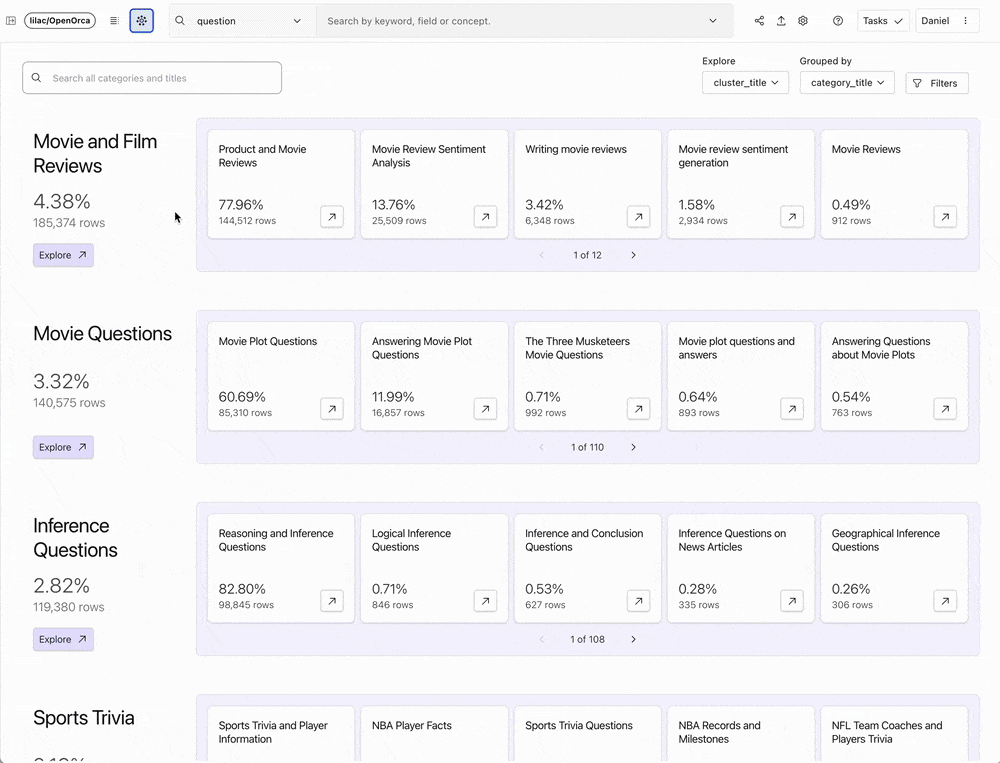
This is useful for data scientists to determine whether certain data sets should be used for a model. Ultimately, this improves the model’s output and reduces the time it takes to train.
Combining Databricks and Lilac
Databricks plans to integrate Lilac into its MosaicML technology further. MosaicML was acquired in mid-2023 and has been further developed into a Data Intelligence Engine. This engine runs on the lakehouse to automatically index columns and enhance data partitioning. “Lilac’s technology will make it easier to evaluate and monitor the outputs of their LLMs in a unified platform, as well as prepare datasets for RAG, fine-tuning, and pre-training,” concludes Databricks.
It is unknown how much Databricks is paying for the acquisition of Lilac.
