Google Anthos now allows virtual machines (VMs) to run alongside containers. The update allows users to deliver consistent VM and container services on a single, unified public cloud-connected platform.
Kubernetes-based declarative configuration and policies allow VMs to run alongside containers in Anthos. In addition, enterprises can control self-service deployment, observability and monitoring for both VMs and containers through the Google Cloud console, APIs and command-line interfaces.
Anthos VM Runtime
Anthos VM Runtime forms the basis of the functionality. The solution builds on the open-source KubeVirt technology. The technology aids Kubernetes adoption in cases where existing VM workloads cannot be easily transformed to containers.
Anthos VM Runtime integrates KubeVirt with the Google Anthos platform on bare metal. This should improve the installation and upgrade experience.
In addition, the solution provides tooling for managing VMs with the log and metrics of the Google Cloud operations suite, including dashboards and alerts. The solution also supports multiple network interfaces and integrations of VLAN environments.
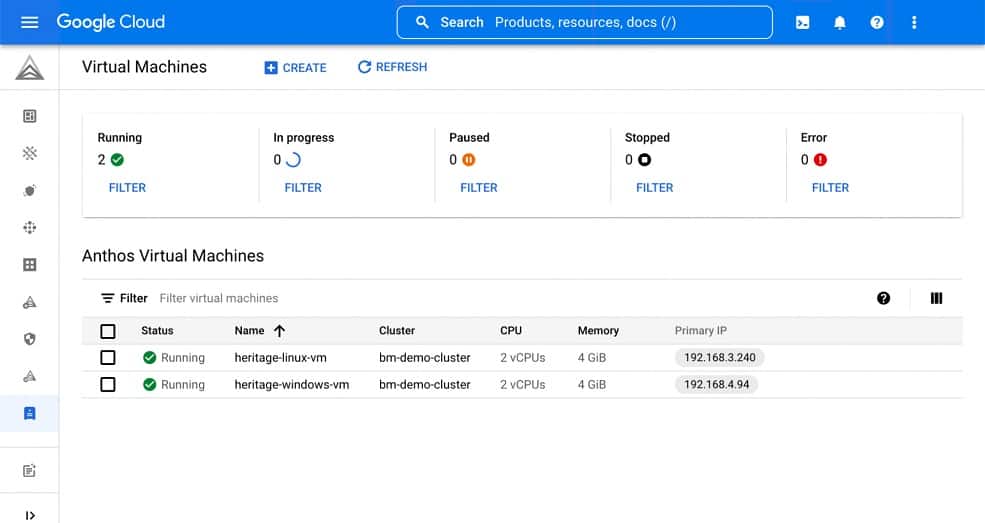
Critical workloads in VMs
Google’s reason for extending Google Anthos is that many companies still run critical workloads in VMs instead of containers orchestrated by Kubernetes.
Some VMs are difficult to transform to containers. A vendor’s application may be incompatible. In other cases, the VM may house data that needs to run in-house for compliance or at the edge for low latency. Furthermore, some companies lack the budget to containerize apps.
Regardless of the reason, Google Anthos VM Runtime should streamline operations for environments that depend on both VMs and containers. Google Anthos VM Runtime is now generally available for bare-metal systems, dubbed Google Distributed Cloud Virtual. Customers can access these systems through their Google Cloud accounts.
Tip: Google Anthos opts for hybrid and multi-cloud with AWS and Azure