Cyber attacks based on Microsoft Excel add-in files (.XLL) increased by nearly 600 percent in 2021. In a new report, security researchers at HP Wolf Security disclose how the file type is being exploited.
Excel add-in files (.XLL) allow DLL files to be opened within Excel sheets. Cybercriminals exploit the feature to spread malware through Excel sheets. In the final quarter of 2021, HP Wolf Security researchers observed a six-fold increase — 588 percent — of XLL attacks compared to the year before.
Attackers distribute .XLL files via phishing emails concerning payment reminders, quotes and delivery statuses. When running the file, users are prompted to download an add-in file. Behind the scenes, the file rolls out malware on the user’s device.
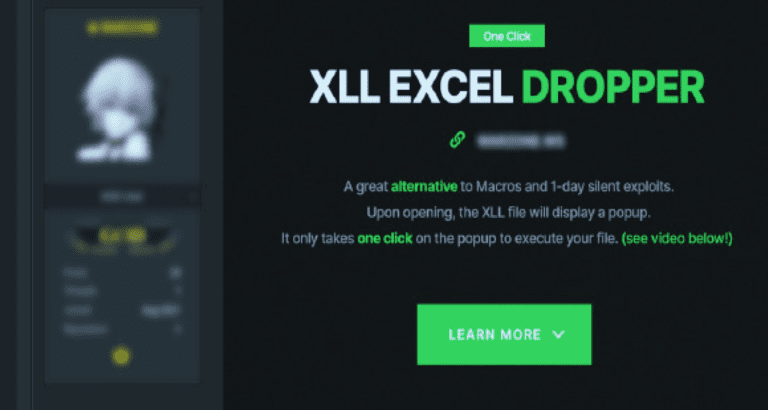
HP Wolf Security found multiple malware types that create backdoors and allow access from outside the device’s network, including BazaLoader, Dridex and Agent Tesla. The researchers stumbled upon a deep web forum post advertising a ‘XLL Excel Dropper’. For $2,000, the advertiser delivers a software product that automatically converts malware links and Excel files into an exploitable add-in file.
HP Wolf Security advises organizations to reject all unknown emails with .XLL attachments via email gateways. The organization urges security teams to remain vigilant for malware distributed with legitimate functions such as Excel XLL.