New Linux-based malware uses 30 vulnerabilities in WordPress plugins to inject malicious JavaScript.
Antivirus vendor Dr. Web reports that the malware comes in two variants capable of attacking Linux-based WordPress sites by exploiting outdated plugins. The first variant found, Linux.BackDoor.WordPressExploit.1, targets both 32-bit and 64-bit versions of the open-source operating system.
How the malware works
The malware is a backdoor that can be remotely controlled to perform several actions. First, it attacks a specific website, enables standby mode, turns itself off and pauses log actions. The tool targets websites that have vulnerabilities in plugins and themes. Website addresses are retrieved from command and control servers.
Secondly, vulnerabilities in plugins and themes are exploited to inject malicious JavaScript code. After the infection, visiting and interacting with the website executes the code. Visitors are typically redirected to pages of the cybercriminals’ choosing.
The malware collects statistics on how many websites it has attacked, how often a vulnerability has been exploited and how often certain plugins have been abused. Furthermore, it informs the cybercriminals’ command and control server about all unpatched vulnerabilities discovered. Dr. Web included a list of all plugins initially affected in its announcement.
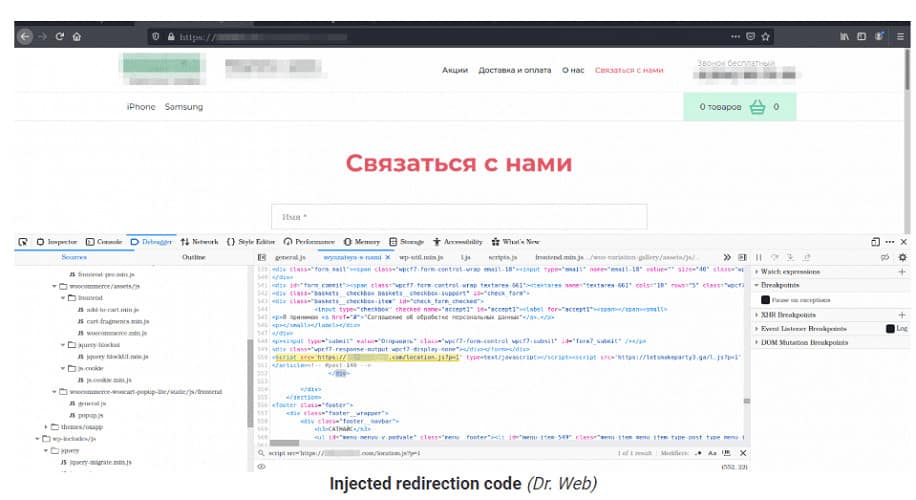
Second variant
The second variant found, Linux.BackDoor.WordPressExploit.2, is an updated version of the variant described above. In this case, the command and control server has a different address and supports additional WordPress vulnerabilities.
Both variants have features that help perform brute-force attacks on WordPress websites with breached login credentials.
The security experts urge WordPress users to keep all components of the CMS system up-to-date, including third-party solutions, adding that administrators should use strong and unique login credentials.