Companies often have dozens or hundreds of databases in use, usually based on different technologies. Managing these databases is extremely time-consuming. Database administrators have to deal with repetitive, lengthy and time-consuming processes, which actually prevents them from doing what they do best. Think about performance tuning, capacity planning and introducing new developments and innovations. This has to be done differently and more efficiently, Nutanix thought. The result is Nutanix Era.
The average database administrator (DBA) has quite a few tasks. The most important task today is to support teams working on innovation. The administrator helps to bring data together, in order to draw conclusions from it. A database administrator can support teams by making data available and giving tips on how to aggregate and use data more efficiently.
However, the fact is that a database administrator is usually not appointed for this purpose. Maintenance is more the reason for appointing a DBA. A DBA has quite a few maintenance tasks. All the databases must remain available, they must be patched and optimisation must take place if necessary. There are quite a few best practices that can be applied to keep a database functioning properly. The big disadvantage of all this is that database management is not automated enough. In most cases, manual optimisation is still involved. This while most organisations have hundreds of databases in use. An automated roll-out of the same configuration to every database is not feasible in most cases. Each database has its own challenges, performance and degree of use. Large organisations, therefore, employ a large number of database administrators. With Era, Nutanix wants to make the DBA’s life easier by automating things.
Also read: Moving to a multi-cloud infrastructure: the financial component
Nutanix Era offers Database as a Service
Organisations have been looking for ways to simplify database management for some time. Until recently, many options were not available. The most obvious example was migrating the database to a cloud environment. All hyperscalers have a managed database offering. Think about Amazon RDS, Google Cloud SQL or Oracle Autonomous Database.
Although those handle a lot of management tasks, it is not always the desired solution. If you move the database to the cloud, the application that uses it must also move to the cloud. In some cases, running an application in the cloud is many times more expensive than in your own data centre. Not to mention compliance and governance. Is it allowed to just move the data to the cloud?
On-premise Database as a Service
Little tooling is available to support database management in an on-premises environment. Each database technology is unique and requires different configurations and optimisations. This makes the threshold for developing such a product particularly high. In fact, the entire development process for each new database technology must be repeated and extensively tested. This also makes the costs high.
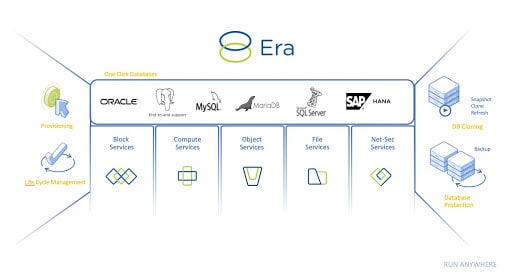
However, Nutanix has not let this stop it and has introduced Nutanix Era. Initially only for Oracle databases and Microsoft SQL Server. This was quickly followed by PostgreSQL, MariaDB and MySQL. In the meantime, there is also support for SAP HANA and MongoDB. With Nutanix Era, a database administrator can create a golden image (template) for each database. The DBA chooses the type of database and the operating system on which the database must run and Nutanix creates a virtual machine with this operating system and the database installed on it. Then Nutanix also applies best practices for that operating system and that type of database. This creates an optimal golden image. The database administrator can then do the company-specific configurations. Then the golden image is ready and can be used to quickly create new databases.
Within the Nutanix HCI platform, a VM can then be created from the golden image with a simple click of a button. Nutanix will also ensure that the VM is well laid out in terms of hard drives, memory and other performance requirements. This makes the database VM run as smoothly as possible on the available infrastructure.
The big advantage of this is that an organisation can quickly make databases available. Separate teams are no longer required for storage, networking, backups and the like. Everything can be done by pushing a button from the Era UI that is integrated with Nutanix Prism, Nutanix’s control panel. It is also possible to develop your own UI and use APIs to connect to the Era UI.
PostgreSQL, MariaDB, MySQL and MongoDB are open source databases and also the easiest to deploy. Within Nutanix Era, the latest versions of these open source databases are available and can be deployed with the push of a button. Nutanix provides templates for this. A company does not have to create a golden image itself. For Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server and SAP HANA this is different because these require licenses. The customer has to upload and create them himself.
Database administrator is not redundant
For those who wonder whether this will not make database administrators redundant: this is not the case. Each application has its own challenges, also on database level. A database administrator can often ensure that a database works better for an application by making configuration changes, simply by adjusting some parameters. Nutanix makes it easier to quickly change those configurations and simplify management. The expertise of a database administrator will always be needed.
It is possible that in the future Nutanix will be able to carry out more optimisations automatically, but that remains to be seen. However, the database administrator will not become redundant any time soon. Ultimately, the advisory role of a database administrator will become increasingly important. Think about how you handle data efficiently and how you can use databases more effectively.
Nutanix Era takes over patch management
Something that database administrators spend a lot of time on is patching the database servers. Almost every month updates appear that solve bugs and security problems in the database software. Features are also added regularly. To keep the software safe and to make new features available, the software must be updated to the latest version.
This may sound like a simple task, but it involves a lot of work. First of all, the database administrator must do this manually for each database. In addition, some database technologies, including Oracle, have a fairly complex upgrade procedure. Nutanix Era responds to this by taking the patch management out of your hands. By pushing a button a database administrator can order a database server to be updated. Nutanix’s advanced cloning technology also comes in handy in this situation. The database administrator can easily make a clone of the database before it is patched. In this way, a good test can be done before updating a database that is running in production.
Since the last version, an Oracle database can be upgraded in its entirety to a new version with one push of a button. For example, from Oracle 12.2 to Oracle 19.
Currently, the VM on which the database runs is not yet updated automatically. This should change in the future. In the near future Nutanix wants to take on the complete patch management.
Nutanix Era vs Ansible
Many database administrators will now wonder what the added value is compared to Ansible, for example. With Ansible you can also patch 100 databases at the same time. The big advantage of Nutanix Era is that you work with a standardised golden image. This gives you the certainty that if a patch works on the first few database servers, it will also work on all the other database servers. If you deployed everything via Ansible and then changed it afterwards, databases can suddenly react very differently. So you will have to test those Ansible playbooks extensively first, which is very labour intensive.
Best practices make the difference
Besides simplifying and automating database management, it’s clear that Nutanix’ best practices make the difference. When an organisation creates a database via Era, all best practices are automatically applied. As a result, a database works optimally and efficiently and the instance is spread across multiple disks that need to deliver optimal performance.
Although Era is able to detect databases running on the HCI platform, it cannot apply best practices to them. They really need to be migrated to the Era platform first. Nutanix cannot tell us yet if there will be a migration tool for this. It is wise to create every database in Era for maximum compatibility with the platform. There are already possibilities to use database backups to migrate a database to Era, for example for SQL server.
Backups and point in time recovery
Another big challenge for many database administrators is making backups. Within Nutanix Prism, this can be done with a few clicks. Nutanix can make backups very quickly through its cloning technology within the HCI platform. The transaction logs are also stored so that a recovery can be carried out to the nearest second, in case something goes wrong unexpectedly. Era calls this snapshot solution TimeMachine. By using the Zero-Byte Clone Technology it is possible to make clones of the databases quickly and without consuming extra storage. This can be done on-demand but also planned.
All features available everywhere
The features of Nutanix Era can differ per database technology. Each database works slightly differently. Therefore, some processes are much more complex or perhaps even impossible because the technical basis is lacking. Nevertheless, Nutanix wants to make all features available for all different database technologies. So the end-user can rest assured that the database management with Nutanix Era is in good hands.
Competition lags behind
The competition is still far away for Nutanix Era. We hear very little from companies with a similar strategy. The biggest competition is probably in cloud-native database technology, although it is now clear that most companies will not become cloud-only. Most companies go for hybrid cloud and then a Nutanix infrastructure is very interesting. Especially for efficient database management.
Also read: What is Nutanix and how it conquers the hybrid and multi-cloud world