Google Cloud recently introduced new security and management capabilities for its public cloud environment. In addition to the launch of the new Workforce Identity Federation service, the tech giant updated GKE Autopilot, a tool that automates container infrastructure management.
The new functionality should help companies secure and manage their cloud environments more easily. The new Workforce Identity Federation service provides customers with more identity management capabilities for their cloud infrastructure.
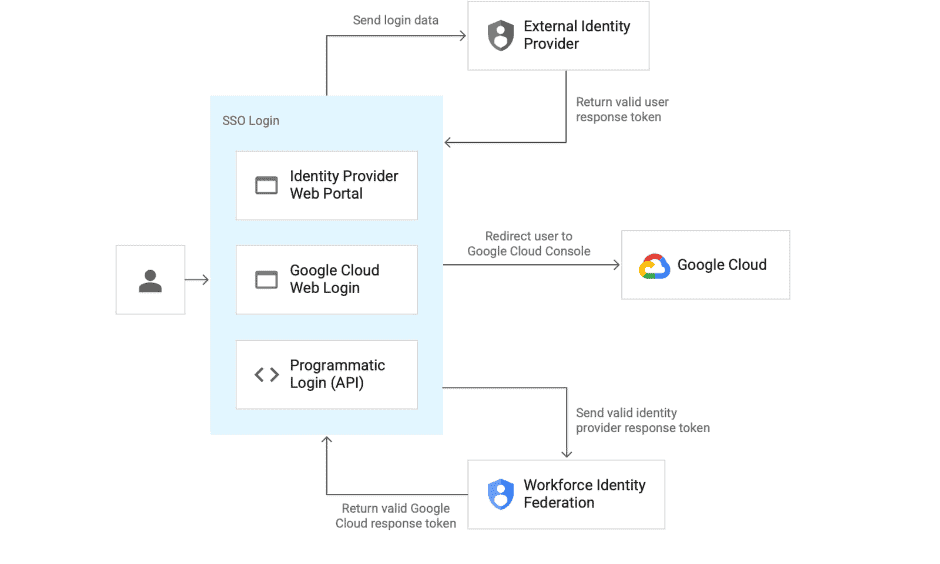
Workforce Identity Federation adds functionality to the tech giant’s existing Identity Management (IAM) service. The service allows companies to centrally control which employees are granted access to cloud infrastructure, which parts of the infrastructure are accessible and how users can connect. The new service should reduce the amount of work required to manage employee access.
Workforce Identity Federation functionality
Security administrators often use IDP platforms to manage employee access to infrastructures. The platforms store the data defining which employees have access to which components.
In the past, administrators had to upload a copy of this data to Google Cloud. The introduction of Workforce Identity Federation eliminates the need to create and manage two identical data sets.
The tool ensures that Google Cloud has the same login experience as the existing IDP for single sign-on. This simplifies and speeds up the management of employee access to applications.
GKE Autopilot
In addition to the identity management solution, Google Cloud introduced new functionality for GKE Autopilot. The tool helps companies automatically set up and manage the cloud infrastructure on which containers run.
GKE Autopilot is part of Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE’s), the tech giant’s container orchestration platform. The update allows companies to set up cloud instances based on Nvidia T4 and A100 GPUs. These GPUs are well suited for various high-performance AI video processing solutions.
By supporting these GPUs, Google allows customers to leverage GKE features for new cloud use cases such as the automated management of container clusters running complex workloads.
Furthermore, customers can now more easily adjust the number of GPUs allocated to containers with a few lines of code. Users no longer have to install drivers to do so. Additionally, GKE Autopilot now automatically takes care of GPU configuration and pod placement completely. Customers no longer have to worry about non-GPU pods running on valuable GPU nodes.
Google Cloud also increased the number of virtual processors (vCPUs) that can be added to a Kubernetes pod. Pods can now have a maximum configuration of 244 vCPUs (up from 54 vCPUs) and 851GB of memory.
Cloud Spanner and Natural Language API
Cloud Spanner gained new functionality as well. The managed relational database can now handle up to twice as many data operations. Lastly, the Natural Language API received an update that improves AI content classification allowing users to sort documents by topic. The new AI capabilities support ten additional languages.
