SAP Datasphere is the evolution of Data Warehouse Cloud. The new product should make it easier for companies to access both SAP data and non-SAP data.
At a pre-launch press conference, CTO Juergen Mueller and CMO Julia White explained Datasphere. According to White, companies are increasingly using data, but seamless access to data is still difficult. That’s why SAP is coming out with a new product, which also directly involves a number of strategic partnerships with major data players.
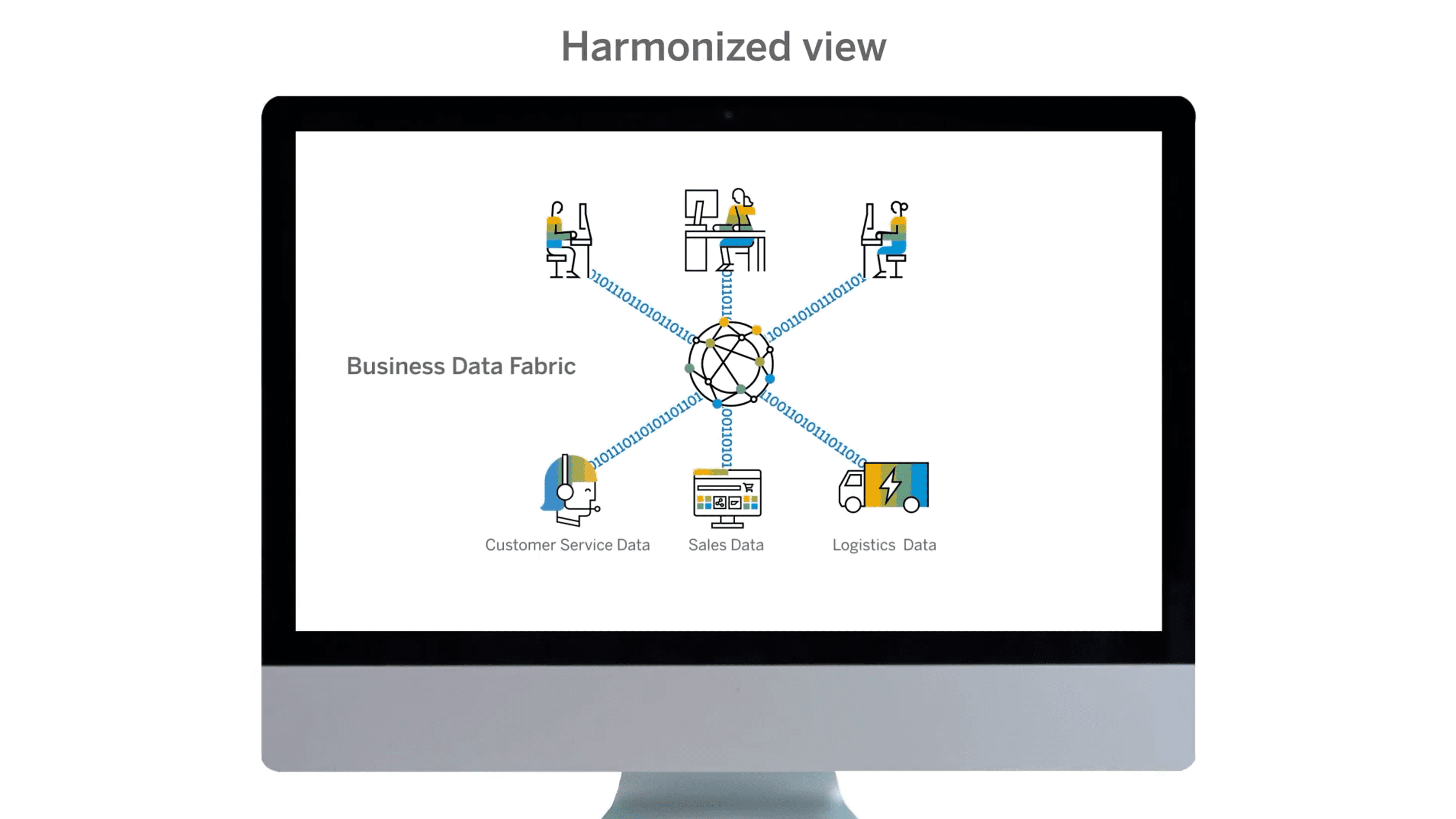
Data Fabric architecture
Mueller says that with SAP Datasphere, users realize a Data Fabric architecture. We pretty much first encountered this concept with NetApp, the storage vendor that also partners with SAP. Basically, NetApp wanted to use this to connect different clouds. Such a data fabric unifies data management of different resources, to achieve consistency and control around security, visibility, access and mobility of the data.
SAP is also focusing on this by building a Data Fabric architecture. “Until today, accessing and using data located in disparate systems and locations – across cloud providers, data vendors and on-premise systems – has been a complex challenge. Customers have had to extract data from original sources and export it to a central location, losing critical business context along the way and recapturing it only through ongoing, dedicated IT projects and manual effort. With today’s announcements, SAP Datasphere helps eliminate this hidden data tax, enabling customers to build a business data fabric architecture that quickly delivers meaningful data with business context and logic intact,” reads SAP’s statement.
It is important to note that Datasphere is the next generation of Data Warehouse Cloud and is built on the Business Technology Platform. This also gives users access to the data integration capabilities of the BTP. Organizations’ SAP systems naturally contain a lot of business-critical data, but third-party systems also contain a lot of valuable data. With that non-SAP data, Datasphere promises to provide more connectivity.
Tip: The SAP Business Technology Platform grows rapidly: what can developers do with it?
Dependence on ecosystem
To make this possible, a slew of new collaborations are also being announced. For example, there will be a strong technical link with Databricks’ lakehouse. Companies that rely on the lakehouse architecture have a lot of data housed in that environment. The Databricks platform is designed for storing, understanding and analyzing data. Users can share data while maintaining semantics. Data is understood as intended regardless of which application or system it comes from. The integration removes confusion and errors in data sharing.
Another collaboration that supports the introduction of Datasphere is with Confluent. This party will integrate its data streaming platform with Datasphere, allowing companies to merge valuable data from different departments, systems and applications into one and use the data in real-time. Confluent’s platform focuses on data in motion to support real-time data from different sources within a company.
Belgium’s Collibra is another partner directly involved in the launch. The customized integration between the data catalog player and SAP provides organizations with an overview of all the data they own. They also see the connections between the data. Such insight is necessary for determining data management strategy.
Furthermore, DataRobot is a direct partner. This gives companies the ability to leverage automated machine learning capabilities for multiple data sources on top of Datasphere. They can integrate these directly into their Data Fabric, regardless of the cloud platform they use.
Building out a solid foundation
By continuing to develop Data Warehouse Cloud and relying on BTP and collaborations, Mueller and White are confident. They promise to offer the following new features:
- Automated data cataloging.
- Simplified data replication to deliver data and its constant updates in real-time.
- Improved data modeling that preserves the context of data in SAP applications.
- Additional application integration capabilities to link data and metadata from SAP cloud applications to SAP Datasphere will also be available in the near future.
We note from what Mueller and White have said that there is plenty more to come as well. So the features and ecosystem will certainly continue to grow. SAP does make companies that use Data Warehouse Cloud automatically customers of Datasphere. So companies can start using the new product right away.