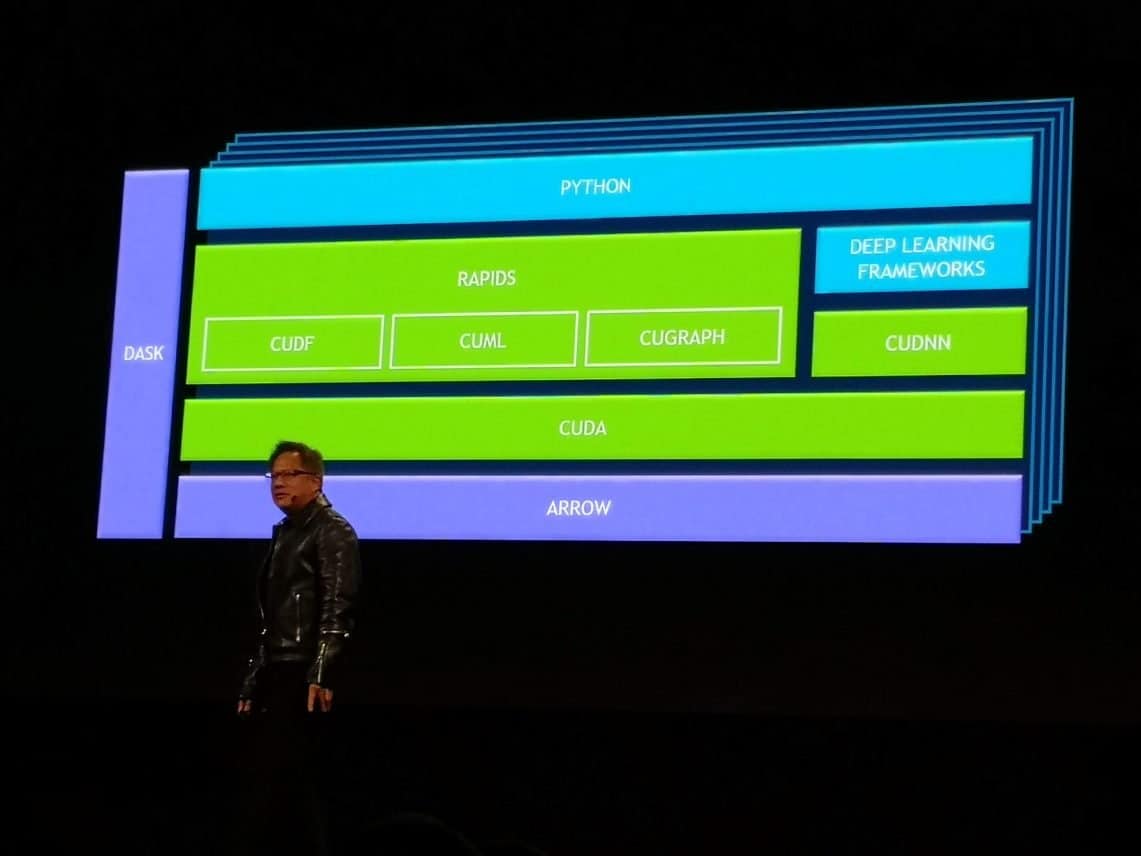
Nvidia launches the open source GPU acceleration platform Rapids during its GPU Technology Conference in Munich. Companies can use the data science and machine learning platform to analyse huge amounts of data more quickly. This enables them to make business forecasts faster and more accurately than is possible with CPUs.
This is a logical step for Nvidia, says Jeff Tseng, who oversees the AI efforts of the chip manufacturer. We have an architecture designed to handle large amounts of data, referring to the parallel computing power of GPUs, which is much more suitable for big data analytics and machine learning than the sequential computing power of CPUs.
Rapids includes open source libraries for GPU-accelerated analytics, machine learning and soon also data visualization. For the first time, the entire data science pipeline can be executed on GPUs. This offers an enormous boost in performance for tackling complex business challenges, such as predicting credit card fraud, inventory forecasting and a better understanding of purchasing behaviour.
50 times faster
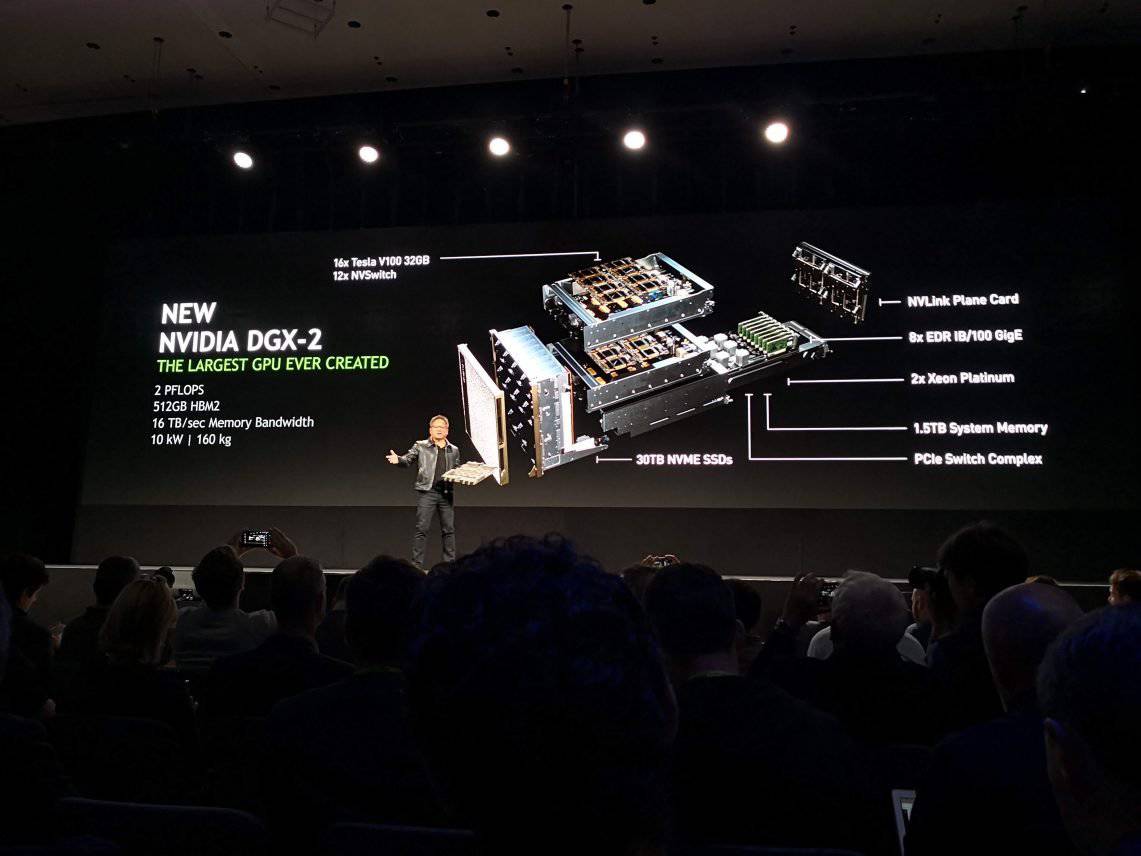
Whereas CPU systems, depending on the dataset, can take hours to days to prepare models for machine learning, Rapids can even reduce that process to minutes, says Tseng. Initial benchmarks on a Nvidia DGX-2 system show up to 50 times faster performance.
These faster performances are not just Nvidia rolling in the muscles, but they also deliver concrete business benefits. Tseng illustrates it with a simple example of a supermarket that has poor visibility of its goods every few days. Excess stock costs a lot of money and means that food is wasted. Too little stock means that the supermarket loses customers. With inventory forecasting, the supermarket can predict its necessary stock on the basis of data.
In inventory forecasting, dozens of data points are collected. This data needs to be cleaned and prepared for use in a machine tooling model, which then needs to be trained. With a CPU system, this process quickly takes a few days, but with GPU acceleration, it is reduced to a few hours. This allows the grocer to make much quicker and more accurate decisions about his stock.
Open source
The Rapids platform is built on CUDA and fully open source. The code is made available under the Apache license. In addition to individual libraries, Rapids container versions are also offered for deployment in the cloud.
The software integrates seamlessly with the most popular open source data science libraries and frameworks, such as Apache Spark. Nvidia has taken the most popular python and machine learning libraries including Apache Arrow, Pandas and scikit-learn and added GPU acceleration.
The green chip giant is working with various partners in the open source communities to expand the number of compatible libraries even further.
Early adopters
Nvidia has already attracted a number of leading enterprises that have started working with Rapids as early adopters. HPE is already using GPU acceleration for its AI and data analytics solutions, IBM has embraced the technology for its machine learning tools for enterprises, and Oracle added support to its cloud infrastructure.
Companies such as Cisco, Dell EMC, Lenovo and Pure Storage have also announced plans to integrate Rapids into their systems in the near future.
This news article was automatically translated from Dutch to give Techzine.eu a head start. All news articles after September 1, 2019 are written in native English and NOT translated. All our background stories are written in native English as well. For more information read our launch article.