AMD recently announced Ryzen Embedded V3000, an energy-efficient processor series for datacenter appliances. The chip manufacturer wants to get an edge on Intel and other competitors.
The Ryzen Embedded V3000 processor series features more cores and memory to deliver better performance than the previous V1000 and V2000 series. The embedded processors are based on the Zen 3 architecture. According to AMD, the processors are especially suitable for storage and networking appliances in datacenters, but can also be built into industrial and edge devices.
Features
The Ryzen Embedded V3000 processor series initially comes in five flavours with four, six or eight cores. The processors’ power efficiency differs from previous Ryzen Embedded Cores series, AMD indicated. The ‘thermal design power’ of the V3000 series ranges from 10 watts to 54 watts. The processors are attached directly to motherboards instead of sockets.
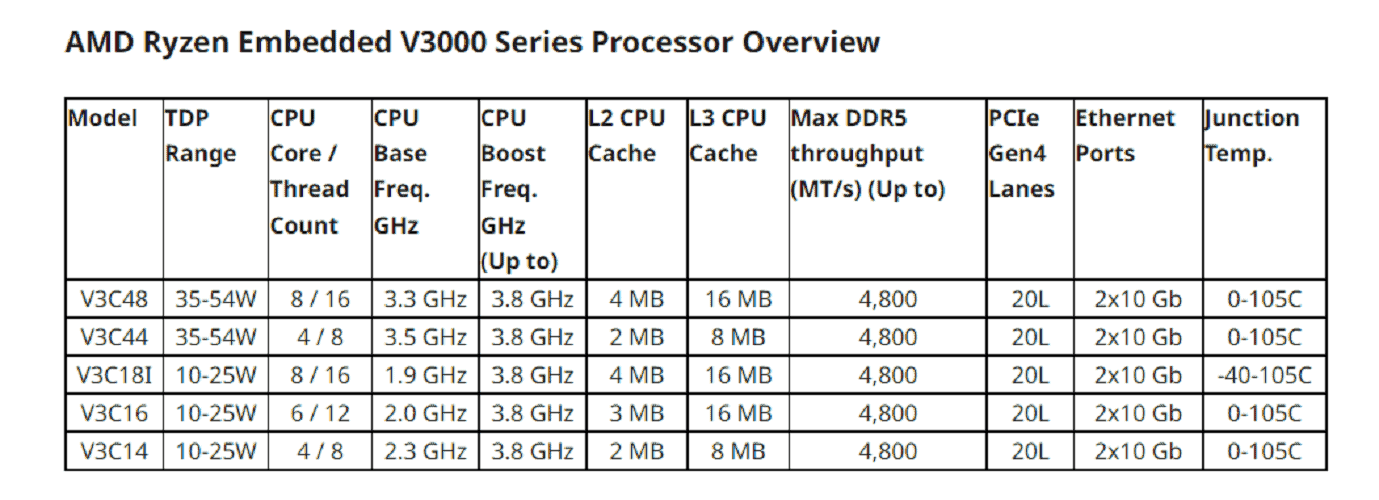
All five processors support DDR5 ECC memory, up to 20 PCIe Gen4 lanes and dual 10 Gbps Ethernet. Furthermore, the processors support Linux with upstreamed Ubuntu and Yocto drivers, as well as AMD Memory Guard security functionality. This technology ensures that unauthorized memory access is blocked. AMD Secure Boot protects against advanced persistent threats (APTs) that target firmware.
Competition with Intel
With the arrival of the Ryzen Embedded V3000 series, AMD seems to be stepping up its competition with Intel, the leading manufacturer of embedded processors. Intel’s Xeon D and industrial Core series feature popular models. Time will tell if AMD manages to knock Intel off its throne.
