The new Windows 11 22H2 update introduces Enhanced Phishing Protection. The functionality alerts users that input their login credentials into unsafe applications and websites.
Windows login credentials allow cybercriminals to access to corporate networks, steal data and launch ransomware attacks. Hackers typically conduct phishing attacks to trick users into providing their login credentials. Sometimes, attackers steal login credentials stored in insecure applications like word processors and spreadsheets.
Enhanced Phishing Protection
Microsoft is attempting to address the problem in the recent Windows 11 22H2 update. The tech giant launched Enhanched Phishing Protection, a set of features that warn users when they input their credentials into unsafe applications and websites.
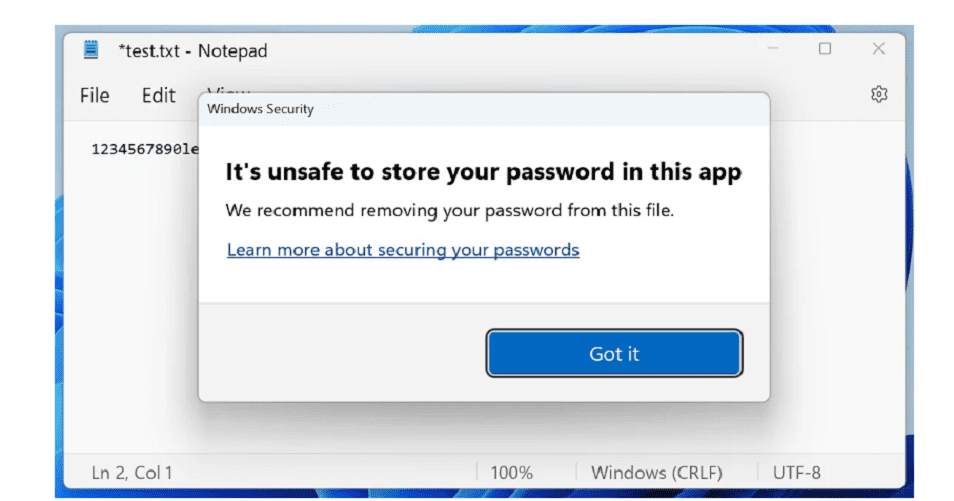
The functionality is based on SmartScreen technology. When users enter their password in an unsafe environment, an alert pops up. In the case of a website, the alert prompts users to change their password. In the case of an application, the alert prompts users to delete the app.
Functionality
The technology checks whether the password is entered on known phishing websites or applications connected to phishing websites. Other factors reviewed are the reuse of passwords for multiple applications or websites and the input of passwords in Notepad, Wordpad or Microsoft 365 applications. Microsoft noted that IT administrators are able to configure custom scenarios that trigger alerts via CSP/MDM or Group Policy.
Not for everyone
The new functionality is exclusively available for Windows 11 22H2 and disabled by default. In addition, the functionality isn’t available for users that input their credentials through Windows Hello or PINs. Lastly, the functionality reportedly doesn’t work yet for Excel, OneNote and Notepad2.
