Western Digital (WD) will base new high-capacity hard drives on HAMR technology in the coming years. It has announced a migration plan for this purpose. From 2026/2027, mass production of these types of HDDs should have started, after which further development of HMDR HDDs can take place.
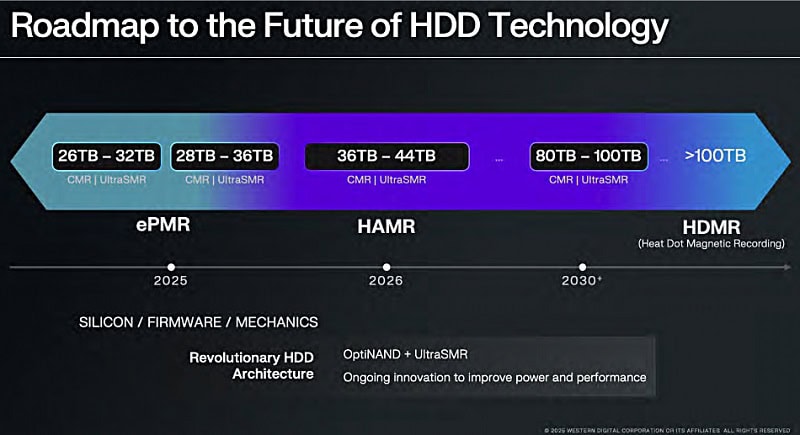
With the growing demand for data center capacity and associated storage, WD is busy advancing its technology. Currently, the company provides up to 26 TB of conventional and 32 TB of shingled HDDs based on its ePMT recording technology. This application uses microwaves to create the old “perpendicular” magnetic recording (PMR) smaller bit environments, allowing more data to be stored.
Making HDDs with larger storage capacities, such as 36 TB to even 44 TB, requires a new technology, namely Heat-Assisted Magnetic Recording (HAMR). This technology temporarily heats the disc material as data is written. This makes it more susceptible to magnetic effects and allows writing data in much smaller regions and with much higher data levels on an HDD.
HAMR roadmap WD
WD therefore announced its roadmap through 2030 for these HAMR HDDs at a recent investor meeting. This year, 28 TB conventional and 36 TB shingled HDDs with ePMR technology are coming to market.
Starting in 2026, the first HAMR HDDs will be available with 36 TB of conventional and 44 TB of shingled storage capacity. Mass production of HAMR HDDs is to be completed in 2026-2027.
Looking ahead to HMR technology
After 2027, WD plans to shift its focus to HDDs that have even higher storage capacity and use HDMR for that purpose.
This storage technology is based on ultra-small, non-inteacting and room-temperature stable magnetic dots. These are heated via a laser, as in HAMR technology, to counteract their resistance to changes in magnetic polarity and thus enable bit value writing. This should eventually lead to more bits being written onto a surface at the nanometer level.
The rollout of these dedicated HMR HDDs is envisioned by WD starting in 2030 and beyond. Using the technology, the HDDs should then have a capacity of 80 GB conventional and 100 TB shingled capacity. Later, the technology should also help produce HDDs with more than 100 TB of storage.
More details spin-off SanDisk
WD also further updated investors on its proposed spin-off of the SanDisk NAND and SSD portfolio this month. The spin-off will be financially based on WD’s equity value that does not reflect SanDisk’s current value. As a result, the HDD vendor hopes the subsidiary will be worth several billion dollars.
Ultimately, with the spinoff, WD shareholders will soon get back the potential profit by 0.33333 shares of SanDdisk for every single WD share they own.
Also read: Western Digital introduces 24 terabyte hard drive WD Red Pro