OpenAI has announced that its chatbot ChatGPT can once again gather information from the Internet. The paid Plus and Enterprise services users have been able to use this feature since Wednesday.
The new capability strengthens ChatGPT’s competitive position against similar chatbots from Microsoft (Bing Chat) and Google (Bard). A salient detail is that Bing Chat runs on the same GPT-4 model as ChatGPT. Microsoft and OpenAI struck a highly lucrative deal after which the former company implemented AI features in numerous products, including Windows 11 and Microsoft 365 applications.
Originally, ChatGPT could access the Internet, but soon OpenAI chose to disable this functionality. It was argued that this was necessary to protect the integrity of paywalls: namely, users could bypass them with the chatbot’s help.
Tip: Microsoft presents Windows 11 23H2 and arrival Copilot
Not the same level of knowledge
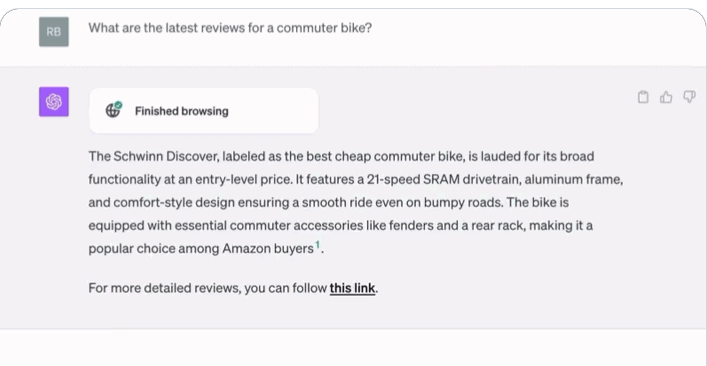
ChatGPT Browsing’s implementation resembles that of its competitors. Like Bard and Bing Chat, the end user can see that the chatbot is first browsing the Web for information. Then, a summarized answer appears, supplemented by footnotes and a link to more reading material.
In this respect, the chatbot’s output differs substantially from regular ChatGPT answers. First of all, there are no source citations present in the conventional answers without Browsing enabled, although the LLM can provide a relatively generic explanation of the data it used for the given output. Also, explanations of topics based on the existing dataset (which runs until January 2022) tend to be more comprehensive, and follow-up questions may lead to a refined output from ChatGPT. It can be seen on X that the Browsing feature does not lead directly to a smooth flow of current information. So in this respect, Bard and Bing Chat seem better focused on delivering Web results in a streamlined way.
Existing alternative: plug-ins
OpenAI had been offering the Browsing feature for some time in beta form for select Plus users. It previously introduced ChatGPT plugins, which, among other things, allowed support for specific real-time information gathering via other platforms. Everything from planning travel through Expedia and querying calculations through Wolfram became possible by enabling the related plugin. As a result, ChatGPT could already access the Internet in various forms. However, OpenAI has yet to integrate real-time resources beyond the status quo of Microsoft and Google. Perhaps this update is a start to that, but the jury’s still out on whether that is the path going forward.
Regardless, OpenAI has done a lot of tinkering with its popular chatbot. It recently introduced support for describing images in addition to spoken inputs and outputs to make dealing with ChatGPT seem a step more human and provide more accessibility for end users.
Also read: ChatGPT supports voice conversations and accepts images
